How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone piloting, covering everything from understanding the fundamental components to navigating legal and regulatory requirements. We’ll delve into pre-flight checks, essential maneuvers, and advanced camera techniques, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
Understanding your drone’s components is the first step. We’ll explore each part, from the propellers and motors to the flight controller and GPS, clarifying their functions and troubleshooting common issues. This foundational knowledge will build your confidence and allow you to address problems effectively. Safety is paramount, and we’ll cover comprehensive pre-flight procedures, airspace regulations, and emergency protocols to ensure responsible and safe operation.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the different parts of your drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key components and provides a glossary of common terms.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Each component plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. A malfunction in any part can significantly impact performance or even lead to accidents.
| Component | Function | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Provide thrust for lift and maneuverability. | Bent or damaged propellers, imbalance. | Inspect for damage before each flight. Replace damaged propellers. Balance propellers if necessary. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, generating the necessary thrust. | Motor failure, overheating. | Check motor connections. Ensure adequate cooling. Replace faulty motors. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, controlling all aspects of flight. | Software glitches, sensor malfunctions. | Firmware updates, recalibration of sensors. Contact manufacturer for support. |
| Battery | Powers the drone’s components. | Low battery, battery failure, overheating. | Monitor battery level. Use appropriate charger. Allow battery to cool down before recharging. |
| GPS | Provides location data for autonomous flight and return-to-home functionality. | Weak signal, GPS drift. | Fly in open areas with clear sky view. Ensure GPS module is properly connected. |
| Camera | Captures images and videos. | Image blur, low light performance issues. | Adjust camera settings, use image stabilization features. |
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology will enhance your understanding of manuals and online resources.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures acceleration and rotation.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of the motors.
- RTF (Ready-To-Fly): A drone that comes fully assembled and ready to fly.
- FPV (First-Person View): A system that allows the pilot to see what the drone’s camera sees.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera.
- Yaw: Rotation around the vertical axis.
- Pitch: Rotation around the lateral axis.
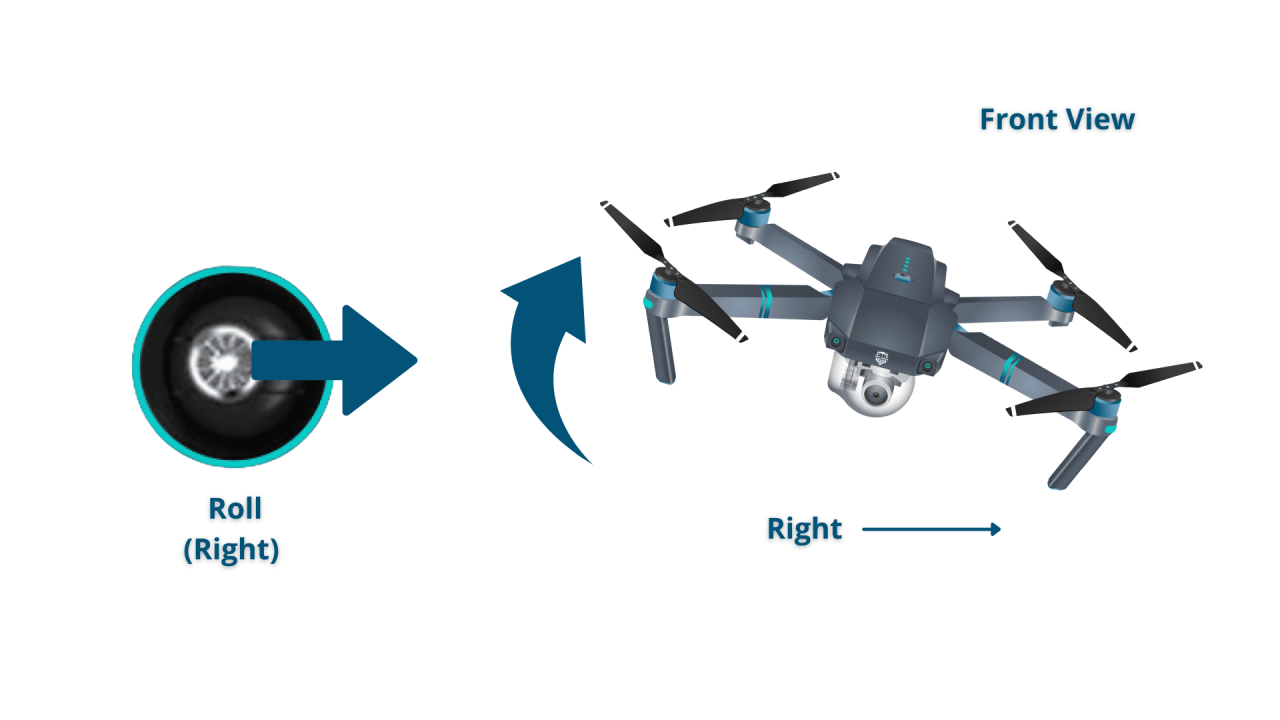
- Roll: Rotation around the longitudinal axis.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount for preventing accidents and ensuring a successful flight. This section Artikels essential steps and considerations.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously follow this checklist to minimize risks.
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Check battery level and charge.
- Ensure GPS signal is acquired.
- Verify controller connectivity.
- Inspect the drone for any visible damage.
- Check weather conditions.
- Identify a safe flight zone, free from obstacles and people.
Safety Procedures and Hazard Mitigation
Understanding and implementing safety procedures is critical for responsible drone operation.
- Safe Flight Zones: Choose open areas away from obstacles, people, and buildings.
- Airspace Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local and national airspace regulations and restrictions.
- Emergency Protocols: Know how to perform an emergency landing and have a backup plan in case of system failure.
- Potential Hazards: Obstacles (trees, buildings, power lines), weather (strong winds, rain), low battery, signal interference.
- Mitigation Strategies: Visual inspection of flight path, weather monitoring, battery management, use of signal boosters.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight process can aid in remembering each step.
[Imagine a flowchart here: Start -> Battery Check -> Propeller Inspection -> GPS Signal Acquisition -> Controller Connection -> Safe Zone Identification -> Weather Check -> Drone Inspection -> Flight]
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are fundamental to drone operation. This section details the procedures for both.
Takeoff Procedure
A smooth takeoff ensures a stable start to your flight.
- Place the drone on a level surface.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition.
- Slowly increase throttle, allowing the drone to ascend vertically.
- Maintain a steady ascent rate.
- Hover at a safe altitude before commencing maneuvers.
Landing Procedure
A controlled descent is equally important for a safe landing.
- Begin descent slowly, reducing throttle gradually.
- Maintain a steady descent rate.
- Approach the landing area gently.
- Reduce throttle to zero just before touching down.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques Comparison
Different drone models may have slightly varying takeoff and landing procedures. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
For example, some drones may utilize assisted takeoff and landing features, while others may require more manual control.
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvering
Understanding and mastering drone flight controls is essential for precise maneuvering and safe operation. This section explains the control inputs and common maneuvers.
Flight Control Stick Functions
Most drones use two joysticks to control flight. One typically controls altitude and direction, while the other controls rotation.
[Imagine a diagram of the joysticks here, showing the functions of each axis: Left stick – Altitude/Direction; Right stick – Yaw/Rotation]
Basic Maneuvers
These maneuvers form the foundation of drone piloting.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude.
- Yawing: Rotating around the vertical axis.
- Pitching: Tilting forward or backward.
- Rolling: Tilting left or right.
Advanced Maneuvers and Wind Management
Advanced maneuvers require practice and skill. Maintaining stable flight in windy conditions requires careful control adjustments.
Examples of advanced maneuvers include flips, rolls, and precise camera movements. In windy conditions, reduce speed, maintain a stable altitude, and compensate for wind drift using the control sticks.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of many drones. Understanding its capabilities and settings is essential for capturing high-quality aerial imagery.
Drone Camera Features
Drone cameras vary in specifications. Key features include resolution, field of view, and image stabilization.
Higher resolution cameras capture more detail. A wider field of view allows for broader shots, while image stabilization minimizes blur.
Camera Setting Adjustments
Adjusting camera settings allows you to optimize image quality for different conditions.
- Exposure: Controls the brightness of the image.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration of exposure to light.
Techniques for High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
Achieving professional-looking aerial imagery requires planning and skill.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds for visually appealing shots.
- Lighting: Shoot during the golden hour for optimal lighting conditions.
- Angles: Experiment with different camera angles for unique perspectives.
- Steady Shots: Use image stabilization features to minimize blur.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is crucial for extending battery life and ensuring safe operation. This section details best practices for battery management.
Battery Care and Maintenance
Following these guidelines will help maintain your drone batteries’ performance.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries.
- Use the manufacturer’s recommended charger.
- Inspect batteries for any signs of damage before each flight.
Safe and Efficient Charging
Always charge batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Use the correct charger and avoid charging batteries in extreme temperatures. Monitor the charging process and disconnect the charger once fully charged.
Signs of a Failing Battery and Recommended Actions
Recognize these signs to prevent potential problems.
- Reduced flight time.
- Swelling or deformation of the battery.
- Unusual heating during charging or use.
If any of these signs are observed, replace the battery immediately.
Factors Affecting Battery Life and Flight Time
Several factors influence how long your battery will last.
- Battery age and condition.
- Temperature.
- Flight style (aggressive maneuvers consume more power).
- Drone weight and payload.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section provides guidance on both.
Routine Maintenance Checklist

Perform these checks regularly to prevent issues.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these stages requires careful attention to detail and practice. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety regulations and practical techniques, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you build confidence and proficiency in operating your drone responsibly and effectively.
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Check motor mounts for tightness.
- Clean the drone body and sensors.
- Inspect battery connections.
- Check for any loose screws or parts.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting Tips
This table Artikels common problems, their causes, solutions, and preventative measures.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power cable issue | Charge battery, replace battery, check power cable | Regular battery maintenance, careful handling of cables |
| GPS signal loss | Obstructions, weak signal | Fly in open areas, recalibrate GPS | Avoid flying near tall buildings or trees |
| Unstable flight | Calibration issues, wind conditions | Recalibrate sensors, adjust flight settings | Regular calibration, avoid flying in strong winds |
| Camera malfunction | Software glitch, camera settings | Restart drone, check camera settings | Regular firmware updates |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. This section highlights key legal considerations.
Drone Regulations and Laws, How to operate a drone
Drone regulations vary by region. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific laws in your area before flying.
Many jurisdictions require registration of drones, restrict flight in certain airspace (e.g., near airports), and have regulations regarding flight near people and property.
Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need permits or licenses to operate a drone legally.
These permits often cover commercial use, flights in restricted airspace, or the use of drones carrying payloads.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial step is learning about pre-flight checks and airspace regulations. For a comprehensive guide on this process, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced flight techniques. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Consequences of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in significant consequences.
These consequences can include fines, drone confiscation, and even criminal charges depending on the severity of the violation.
Safe and Legal Drone Operation in Populated Areas
Operating a drone safely and legally in populated areas requires extra caution.
Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone, avoid flying over crowds, and respect privacy regulations. Check local ordinances regarding drone operation in public spaces.
Mastering drone operation involves a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you’ll not only learn how to pilot your drone proficiently but also how to do so safely and legally. Remember, consistent practice and a commitment to safety are key to unlocking the full potential of your drone and capturing stunning aerial perspectives.
Continue to explore advanced techniques and always prioritize responsible operation.
FAQ Explained
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and comprehensive tutorials.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately initiate a return-to-home (RTH) function if available, or carefully maneuver it back to your location using visual cues.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the model, battery size, and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Consult your country’s or region’s civil aviation authority website for up-to-date drone regulations and airspace restrictions.
